Flexible data placement (FDP) is a possible forthcoming feature of the NVMeTM specification that has been proposed by Google and Meta.1 The purpose of this feature is to reduce the write amplification (WA) when multiple applications are writing, modifying and reading data on the same device.2 Benefits of reduced WA for these companies come in the form of more usable capacity and potentially a longer useful life for each device.
We proposed an experiment to determine how helpful FDP might be. In this test, we are using a 7.68TB Micron 7450 PRO SSD split into four equal (1.92TB) namespaces and executing parallel flexible input/output tester (fio) workloads on each namespace.3 These workloads are all sequential writes but vary in block size (4K, 16K, 64K and 256K). We also execute these workloads individually to four 1.92TB Micron 7450 PRO SSDs, which we imagine as the most optimal implementation of FDP where all application data receives dedicated NAND space and does not get interleaved on the device as shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1
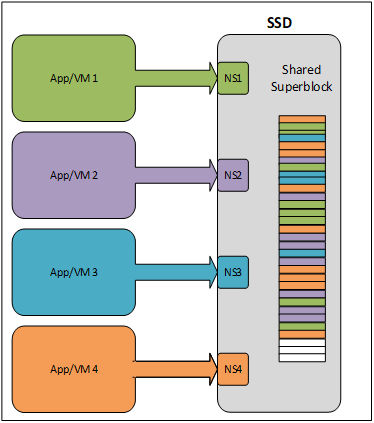
Figure 2

Though this is a simple experiment, it shows the potential benefits for FDP implementation on future devices. We can also see how some applications, which are designed to write sequentially as much as possible, would benefit from FDP when contending for the same drive resources.
1. For additional information on FDP, see https://nvmexpress.org/wp-content/uploads/Hyperscale-Innovation-Flexible-Data-Placement-Mode-FDP.pdf
2. For additional information on write amplification, see https://www.snia.org/education/online-dictionary/W
3. Fio documentation is available here: https://fio.readthedocs.io/en/latest/fio_doc.html
© 2023 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved. All information herein is provided on an "AS IS" basis without warranties of any kind. Products are warranted only to meet Micron’s production data sheet specifications. Products, programs, and specifications are subject to change without notice. Micron Technology, Inc. is not responsible for omissions or errors in typography or photography. Micron, the Micron logo, and all other Micron trademarks are the property of Micron Technology, Inc. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners. Rev. A 01/2023 CCM004-676576390-11635

